Google Tag Manager
Google Tag Manager has three main parts:
Tags: JavaScript particles or tracking pixels
Triggers: This tells GTM when or how to trigger a tag
Variables: Additional information that GTM may need for the tag and trigger to work
What are Tags?
Tags on your website are a line of code that can send important information to some third-party tools like Google Analytics. Tags must be added to every page of your website unless you use a tag manager. Tags are the part that keeps track of what happens on each of your web pages. Tags can understand how users interact with features on your website. Tags are useful when used with a tool like Google Tag Manager, as they can automatically track the information you want and need. The code is actually added to GTM which helps you keep track of the information you want.
The tag manager also has a great feature that can let you know when your code is not working. This makes it easy to go back to the tag manager and realize that you need to fix the code.
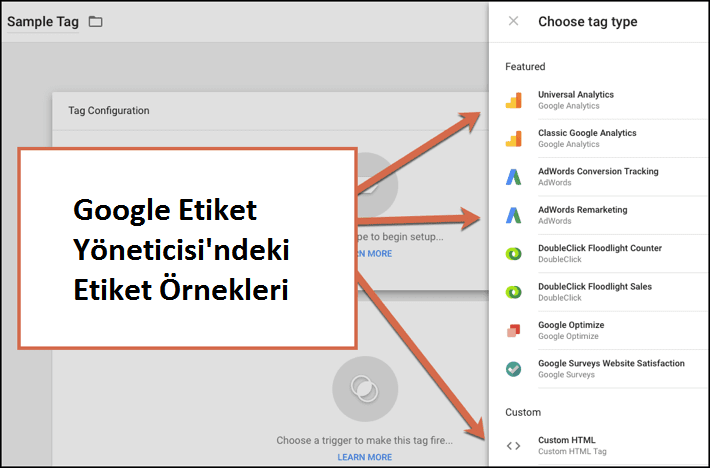
Common examples of tags in Google Tag Manager are:
- Google Analytics Universal Tracking Code
- Ads Remarketing Code
- Ads Conversion Tracking Code
- Heatmap Tracking Code (Hotjar, Crazyegg, etc.)
- Facebook Pixels
What Are the Triggers?
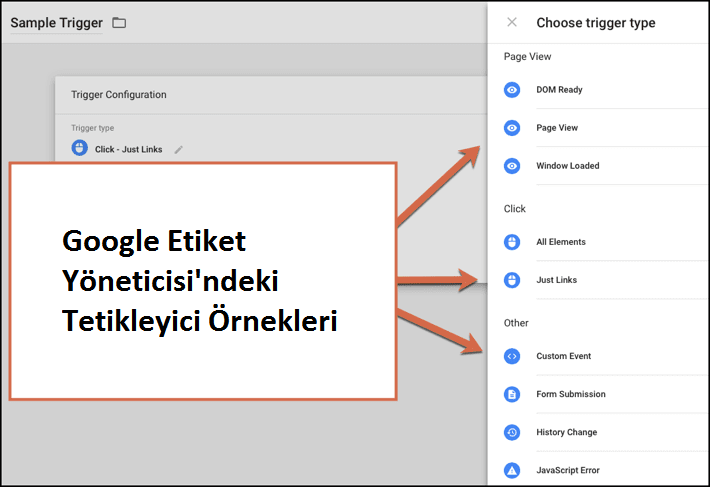
Triggers are another important aspect of using Google Tag Manager. Triggers are events that happen on your page. Tags are triggered when an event occurs on the page. Thus, the information is collected from the label and stored in the location you specify. That's why it's a good idea to have your GTM work with Google Analytics. There are many different triggers a webmaster can choose to collect information from. Triggers can be a user clicking buttons on a website, viewing a specific page, scrolling down to learn more, or downloading something. It may also include when forms are submitted or purchases made. These are just a few examples, but there are many different triggers to choose from with Google Tag Manager.
What are the Variables?
These are variables when Google Tag Manager uses different aspects to figure out if a trigger's condition is met. Variables also have the capacity to send very specific information. You can specify variables or use the option to include all types of clicks when a visitor clicks a link. Use variables if you're interested in tracking certain actions, such as clicks on a single URL. It is important to determine what values will be required for the different variables you want to monitor.
Some variables may include the speed at which a user scrolls up or down on a page, the amount of product they purchase, or how much time they spend on a particular page of your site. These variables can help you track the most important and relevant information needed for marketing or usability purposes. Variables are used with both triggers and tags to help you get the most specific information. It can help rule out junk data so you get exactly what you need when you need it.
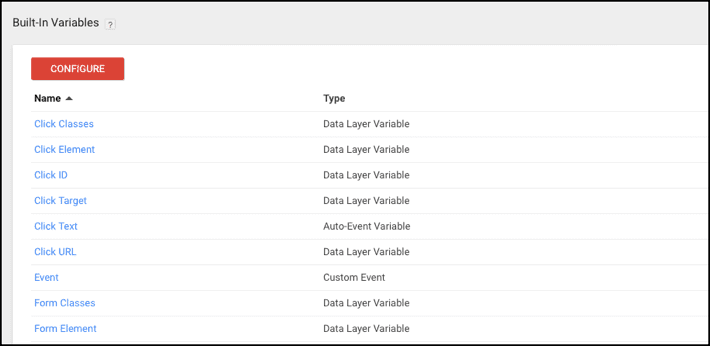
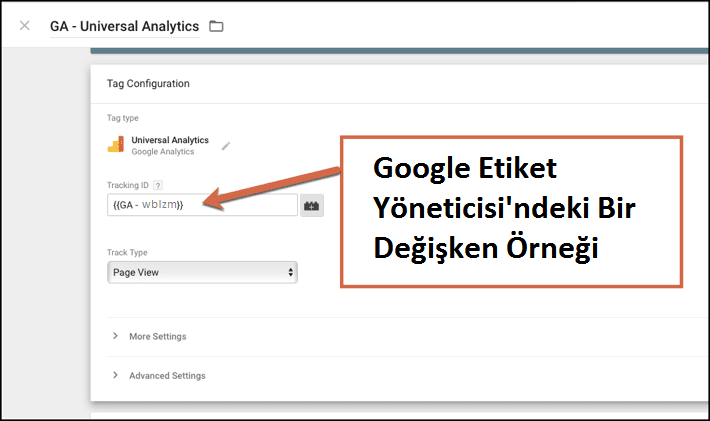
The Google Analytics UA number, also known as the Tracking ID Number, is the most basic type of constant variable that can be created in Google Tag Manager.